Freezer to Freedom - the Milkify Blog

Is Freeze-Dried Breast Milk Safe? Preventing Ba...
With the latest set of infant formula recalls due to bacterial contamination, many parents are wondering: "Should I be concerned about bacteria in my breast milk? And what about contamination...
Is Freeze-Dried Breast Milk Safe? Preventing Bacterial Contamination
With the latest set of infant formula recalls due to bacterial contamination, many parents are wondering: "Should I be concerned about bacteria in my breast milk? And what about contamination...

Ultimate Guide to Freeze-Dried Milk for Travel
Freeze-dried breast milk is a lightweight, shelf-stable alternative to traditional storage methods, making it easier for parents to travel with their baby's nutrition. By removing water content through a specialized...
Ultimate Guide to Freeze-Dried Milk for Travel
Freeze-dried breast milk is a lightweight, shelf-stable alternative to traditional storage methods, making it easier for parents to travel with their baby's nutrition. By removing water content through a specialized...
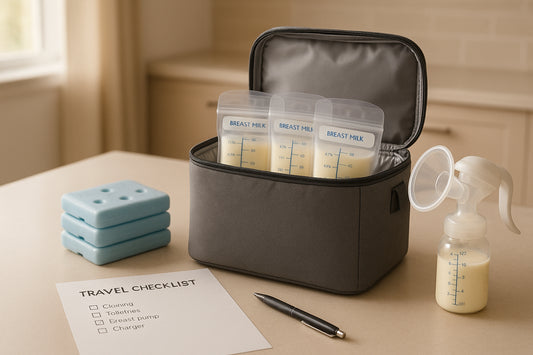
How to Pack Breast Milk for Air Travel
Traveling with breast milk can feel overwhelming, but with the right preparation, it becomes manageable. Here's what you need to know: TSA Rules: Breast milk is exempt from the 3.4-ounce...
How to Pack Breast Milk for Air Travel
Traveling with breast milk can feel overwhelming, but with the right preparation, it becomes manageable. Here's what you need to know: TSA Rules: Breast milk is exempt from the 3.4-ounce...

FAQ: Common Questions About Freeze-Dried Breast...
Freeze-dried breast milk is a way to preserve breast milk as a powder that retains nutrients, lasts up to 3 years, and is easy to store and use. Freeze-drying preserves...
FAQ: Common Questions About Freeze-Dried Breast Milk
Freeze-dried breast milk is a way to preserve breast milk as a powder that retains nutrients, lasts up to 3 years, and is easy to store and use. Freeze-drying preserves...

Breast Milk Soap: Benefits, How to Make It, and...
Breast milk has long been recognized for its healing and nourishing properties. Many parents have discovered its benefits for treating minor skin conditions, from diaper rash to eczema. While turning...
Breast Milk Soap: Benefits, How to Make It, and Safety Considerations
Breast milk has long been recognized for its healing and nourishing properties. Many parents have discovered its benefits for treating minor skin conditions, from diaper rash to eczema. While turning...

5 Common Breast Milk Storage Mistakes to Avoid
Storing breast milk properly ensures it stays safe, nutritious, and ready for your baby. Here’s what you need to know: Use the Right Containers: Stick to BPA-free, commercially available lactation...
5 Common Breast Milk Storage Mistakes to Avoid
Storing breast milk properly ensures it stays safe, nutritious, and ready for your baby. Here’s what you need to know: Use the Right Containers: Stick to BPA-free, commercially available lactation...



